Which Inheritance is Not Supported in Java?
Learn via video course

Multiple inheritances using classes is not supported by Java. Handling the complexity that causes due to multiple inheritances is quite complex. It causes issues during various operations (such as casting, constructor chaining, etc.,) and the main reason is that there are very few circumstances in which we actually need multiple inheritances. Thus it is advisable to ignore it to keep things simple and easy.
It creates ambiguity in the Diamond problem; consider a class A that has a foo() method and then B and C that derive from A and have their own foo() implementation, and now class D derives from B and C using multipleinheritancese and if we refer only to foo() the compiler will not be able to decide which foo() it should invoke. The structure of this inheritance situation is comparable to a four-edged diamond, therefore, it is also known as the Diamond problem.
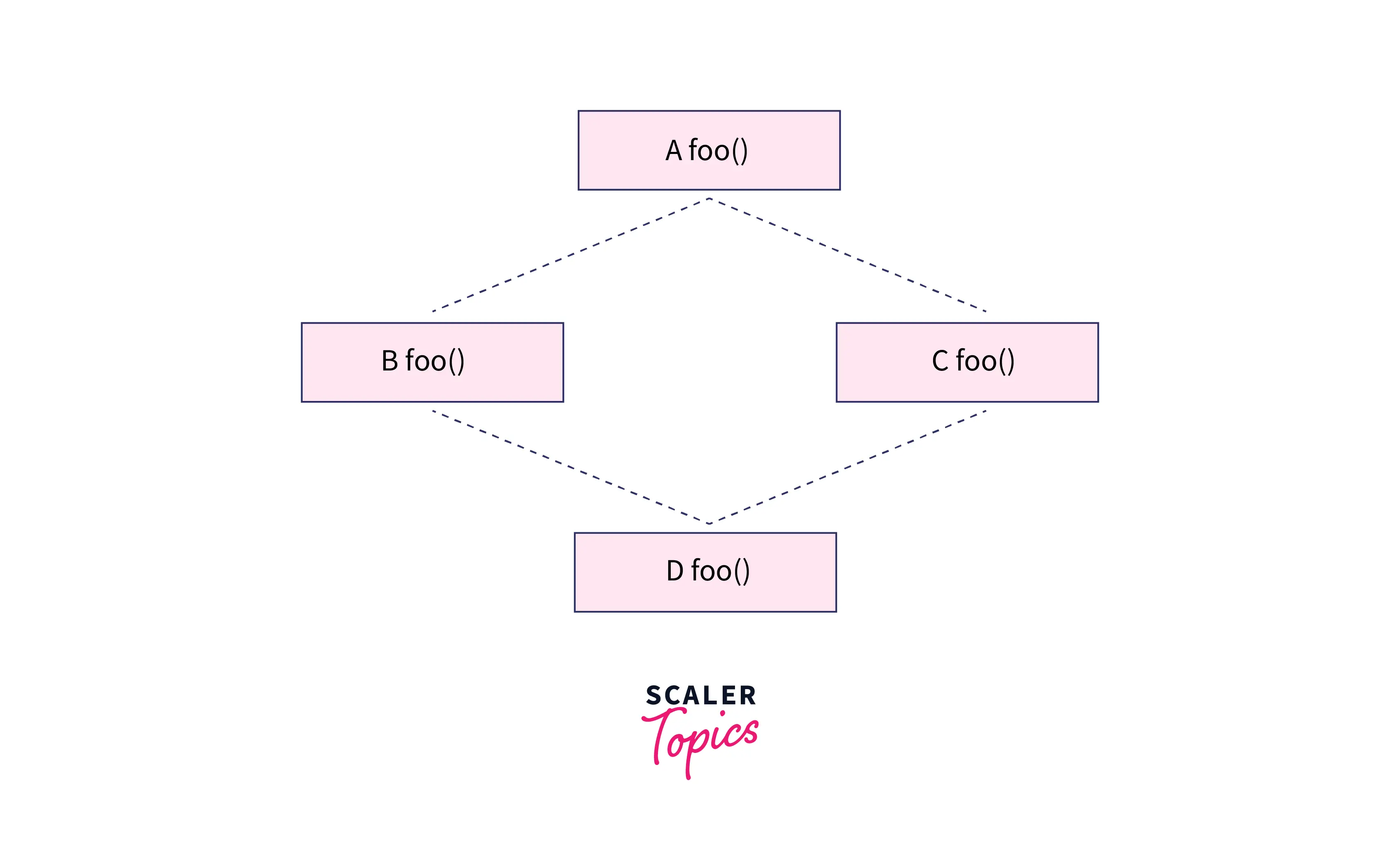 We'll still face this ambiguity problem even if we remove the top head of diamond class A which will ultimately lead to multiple inheritances.
We'll still face this ambiguity problem even if we remove the top head of diamond class A which will ultimately lead to multiple inheritances.
Java avoids this ambiguity by supporting interface inheritance. The interface simply has a method declaration and no implementation, there will only be one implementation of a specific method, so there will be no ambiguity.
Multiple Inheritance In Java
Multiple Inheritance is an object-oriented concept that allows a class to inherit properties from more than one parent class. The issue arises when methods with identical signatures exist in both superclasses and subclasses. The compiler cannot identify which class method should be called or which class method should be prioritized when calling the method.
Multiple inheritances lead to ambiguity. For example, suppose there is a class named Sub and two classes named Super1 and Super2, containing a method named sample (). And if the class Sub inherits both Super1 and Super2, there will be two copies of the sampling method, one from each superclass, and it will be difficult to determine which method to use.

Multiple Inheritance Can be Achieved Using an Interface
An interface is similar to a class that has variables and methods, but the methods in an interface are abstract by default, unlike a class. In Java, multiple inheritances by interface occur if a class implements multiple interfaces or also if an interface itself extends multiple interfaces.
Example: In this example, we will have a look at how a Java program demonstrates multiple inheritances through an interface.
- Each interface, AnimalEat and AnimalTravel has one abstract method, i.e., eat() and travel(). The interfaces AnimalEat and AnimalTravel are implemented by the Animal class.
- An object of class Animal is created in the main () method of class Demo. Then the methods eat() and travel() are invoked.
Output of the above code:

Java Program to Illustrate Unsupportance of Multiple Inheritance
Example 1: In this example, we have two classes, Parent1, and Parent2, both of which contain the same function, fun() (with parameters). A copy of both fun() methods should be made in the subclass object according to the basic rule of inheritance, leaving the subclass with two methods with the same prototype. Then, if you use the subclass object to call the fun() method, the compiler faces an ambiguous situation and gets confused as to which method to call.
As a result, multiple inheritances are not permitted in Java, and you cannot extend more than one other class. Even so, attempting to do so will result in a compile-time error.
Output of the above code:

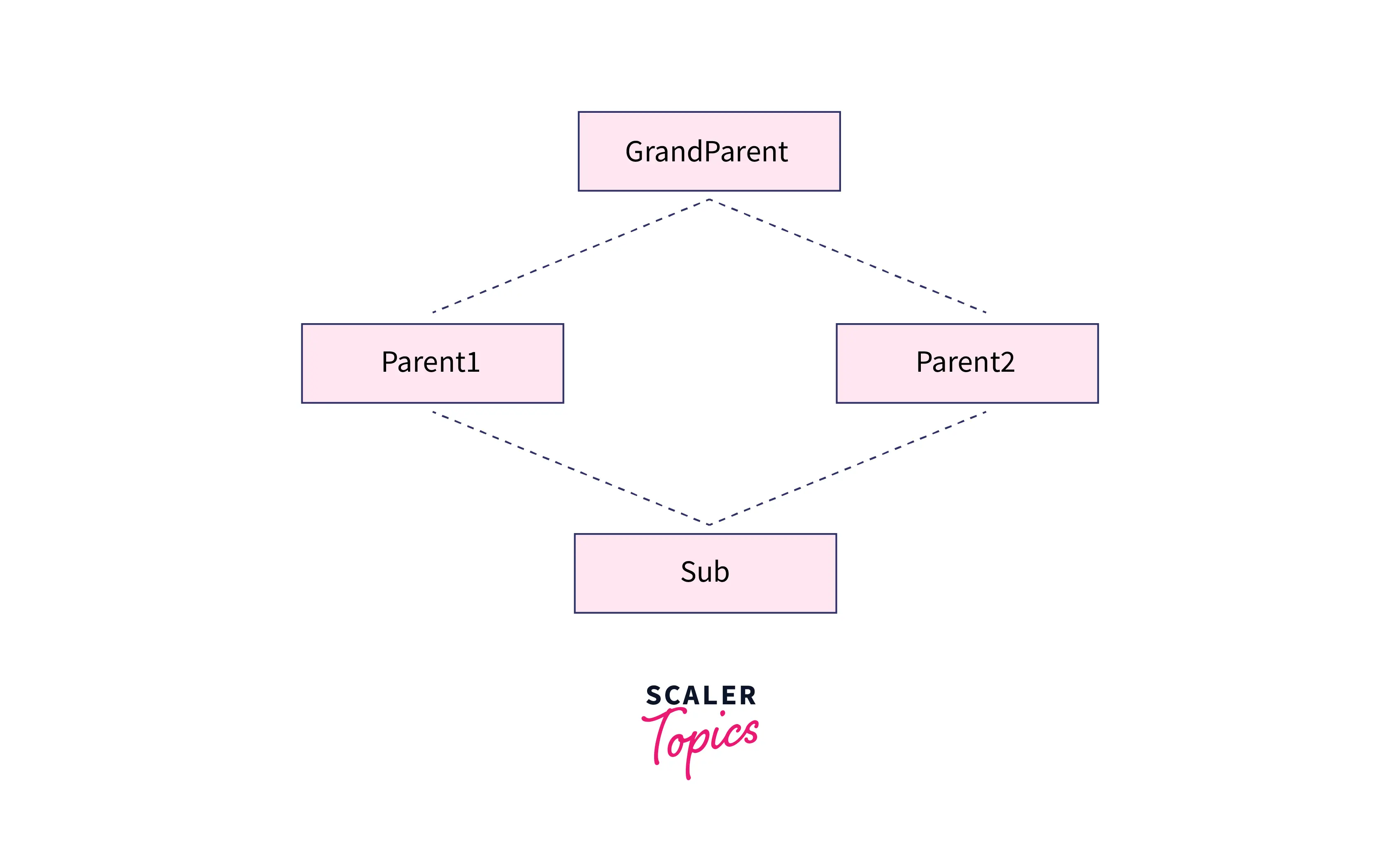
Example 2: In this example, we'll see how the diamond problem is generated by multiple inheritances. Problem arises when we use the Sub object to call the method fun(), such as whether to call Parent1's fun() or Parent2's fun() method. To avoid such complexities, Java does not support multiple-class inheritance.
As a result, when the fun() method is called, it throws another compiler error since multiple inheritances cause a diamond problem, which is acceptable in other languages such as C++`` and Common Lisp`.
Output of the above code:

Learn More
Conclusion
- Multiple Inheritance occurs when the properties and behavior of multiple classes are passed down to a single class. C++ and Common Lisp are some popular languages that allow for multiple inheritances.
- Multiple inheritances is not supported in Java to prevent the ambiguity that multiple inheritances can cause. The Diamond problem is one of the most typical problems caused by multiple inheritance.
- If we wish to implement multiple inheritances in Java, we can do it by utilizing the interface concept in java, which also eliminates the ambiguity problem.
