BFS Program in C
Learn via video course

Overview
BFS algorithm in C, also known as the Breadth-First Search algorithm is commonly used as a searching, traversing algorithm in graphs, trees, multidimensional arrays, or in general recursion. BFS program in C is implemented by using a queue data structure to perform the basic characteristic of the BFS algorithm that is traversing level-wise. BFS algorithm is usually used to find the shorted path or the nearest neighbor element in a graph or tree.
Scope
- In this article, we will learn the basics of the BFS algorithm in C and implement of BFS program in C.
- We will go through the main data structure used in the BFS program in C with an explanation.
- In this article, we will implement BFS only in the C programming language.
Introduction
Imagine a fire breaking down in the jungle, how will it proceed? If we ignore the factor of the wind then, it will go in each direction equally at the same time. Let’s imagine fire breaking on an N*N grid’s center then its path will be like this:
- Initially, fire is at the center: (2,2) (cross represents the fire)

- Now as it will move equally in all directions at the same time means later it will cover (2,1), (2,3), (1,2), and (3,2) at the same time.

- After that, from the point (2,1) it will spread to (2,0), (1,1), and (3,1). Also, it will not go to or revisit point (2,2). Similarly, for the other points other than (2,2) it will spread to other points that are:

Here we can notice one pattern the indexes which are at the same distance from the starting point of the fire break down covers at the same time by the fire. Similarly, the BFS algorithm works, it proceeds with the searching in the level order means to go to the nodes which are at the same distance from the starting node by skipping the visited nodes and finding the shortest path between two nodes.
BFS algorithm in C programming language is mainly used in the multi-dimensional array(mostly 2-D array), trees, graphs, and maybe for normal searching this algorithm can be used.
BFS algorithm is not much efficient with respect to the space but highly efficient in terms of finding the solution. DFS algorithm has the chance to be stuck in infinite search and it may never provide a solution.
Breadth First Search (BFS) Program in C
To implement the BFS algorithm in C users need to store the nodes which are already visited but not processed, for this we will store them in a queue which will provide us the FIFO property (First in First Out). Also, we need to maintain the nodes which are visited, to escape revisiting and reprocessing them. So we will maintain an array to mark visited nodes.
Algorithm:
- Initially, we will add the initial node from where we have to start the search and mark it visited in the visited array.
- Run the while loop until the queue is non-empty.
- At each iteration, find all the connected nodes to the front element of the queue.
- If the connected nodes to the front elements are already visited then do noting
- Else, mark them visited in the visited array and push them into the queue.
Note: These are the basic steps of the BFS in C algorithm, now we can add some special points into the implementation like: If we are searching for a special node then we can end the while loop when we reach the required node.
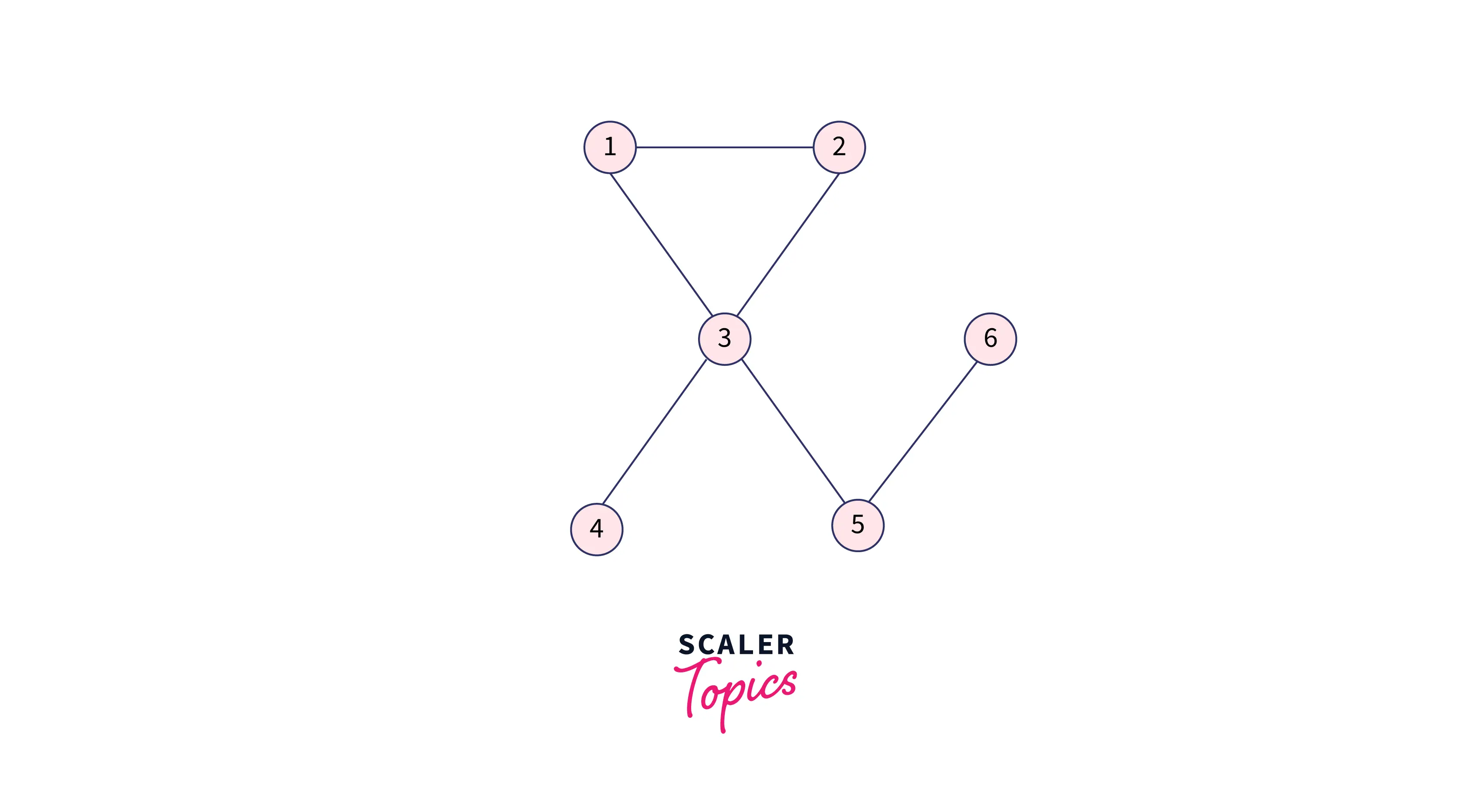
Let’s take an example to show the working of the above-given algorithm: Imagine a graph with six nodes:
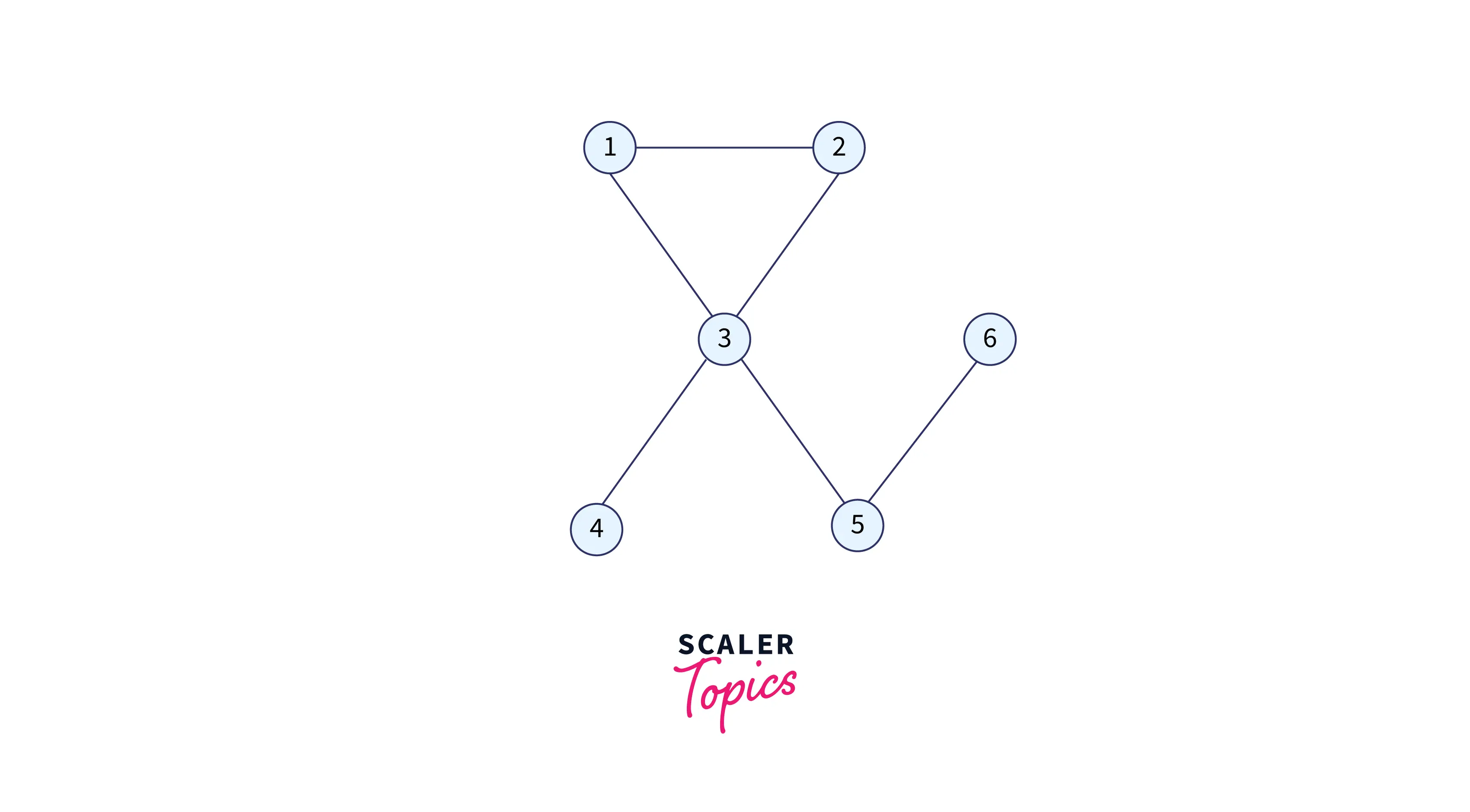
Here,
- 1 is connected to 2 and 3.
- 2 is connected to 1 and 3.
- 3 is connected to 1, 2, 4, and 5.
- 4 is connected to only 3.
- 5 is connected to 3 and 6.
- 6 is connected to only 5.
In starting there is nothing in the queue and all the indexes of the visited array are zero.
As we are going to start Breadth-First Search from 1, we will add it into the queue and make it visited:
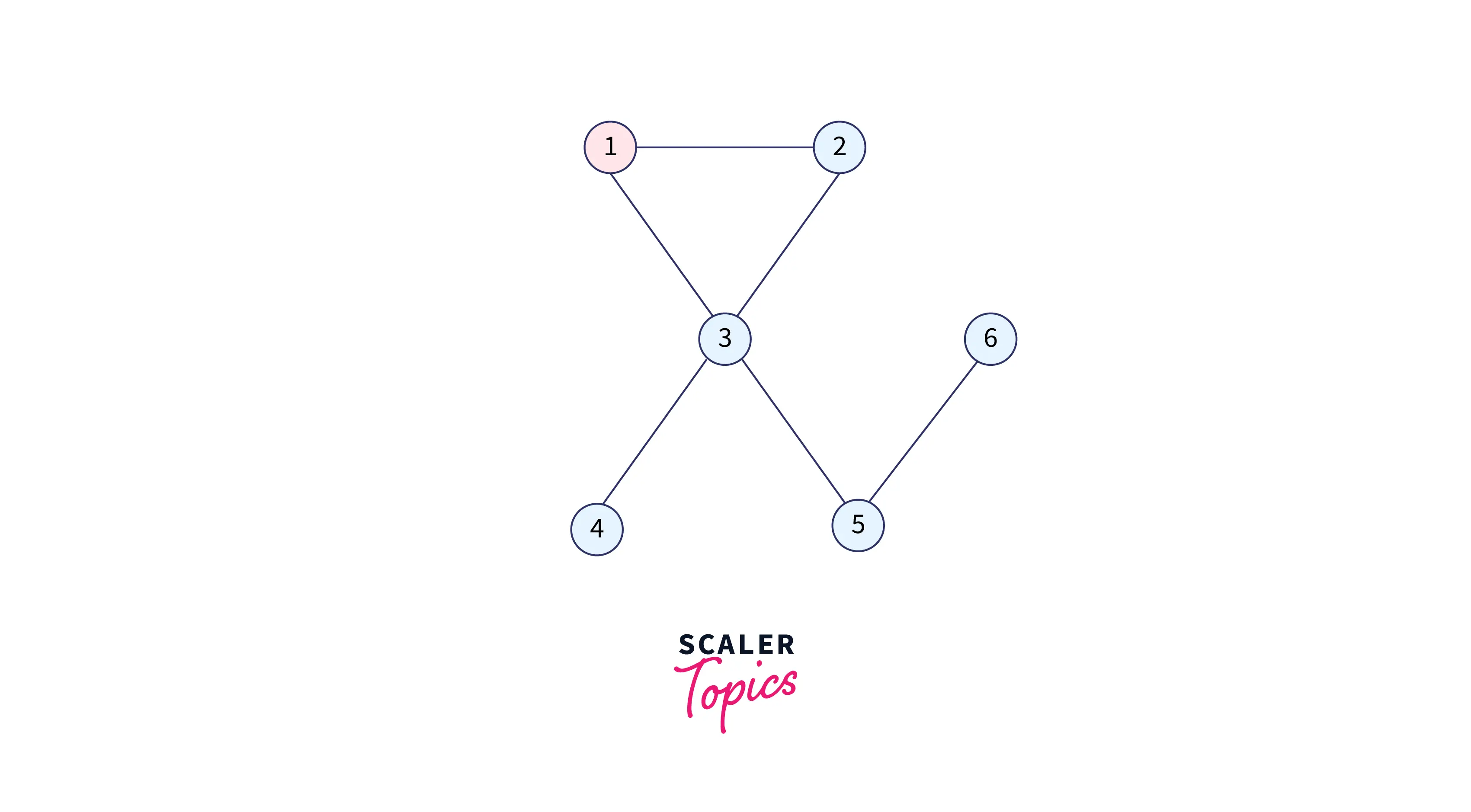
Queue: 1
Visited: 1 0 0 0 0 0
We will process for node 1 and add connected nodes to it that are 2 and 3.
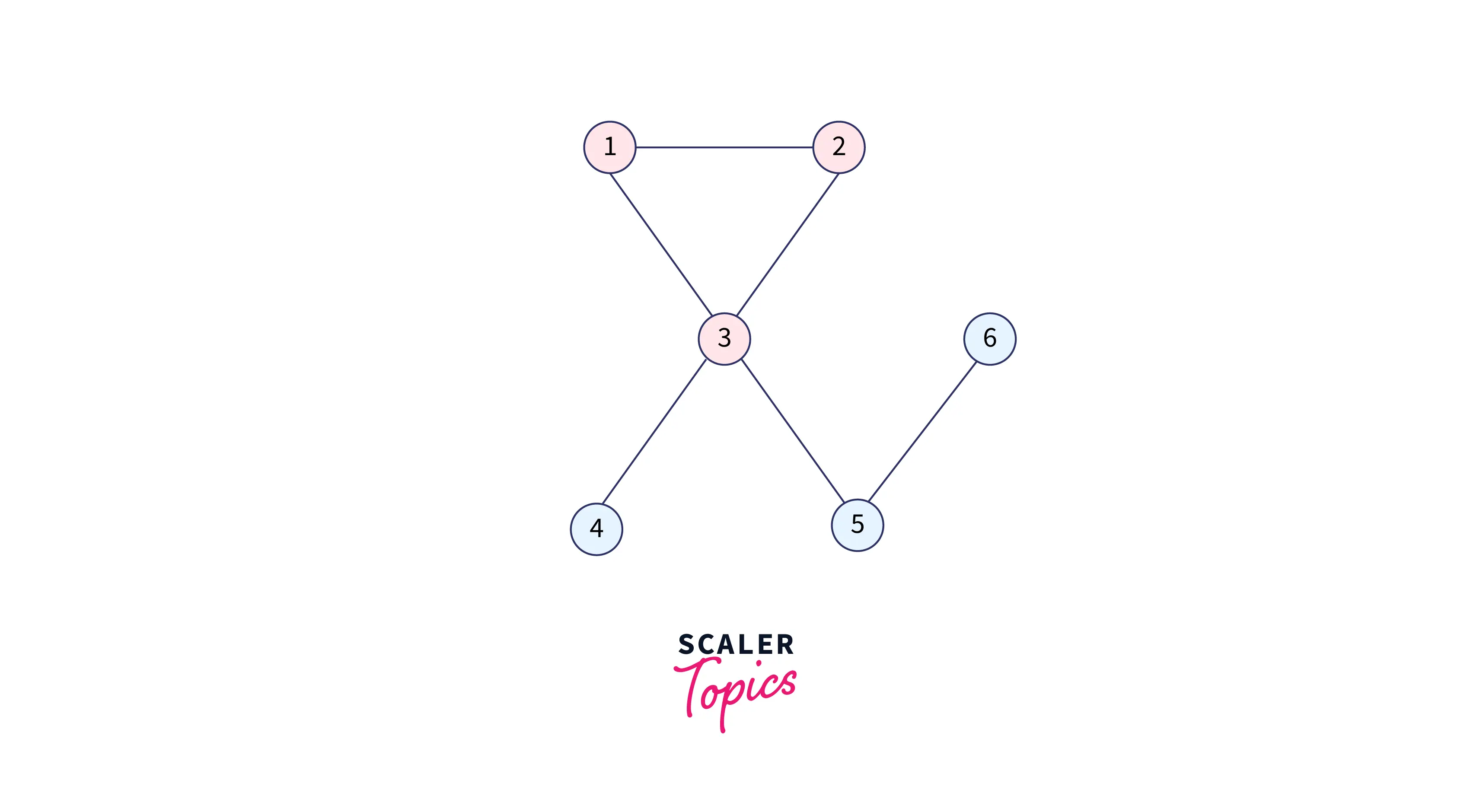
Queue: 2 3
Visited: 1 1 1 0 0 0
Now we will process over Node 2, but both of its connected nodes 1 and 3 are visited so we will simply pop 2 from queue and process on 3.
Queue: 3
Visited: 1 1 1 0 0 0
For node 3: Nodes 1 and 2 are already visited so we will add 4 and 5.
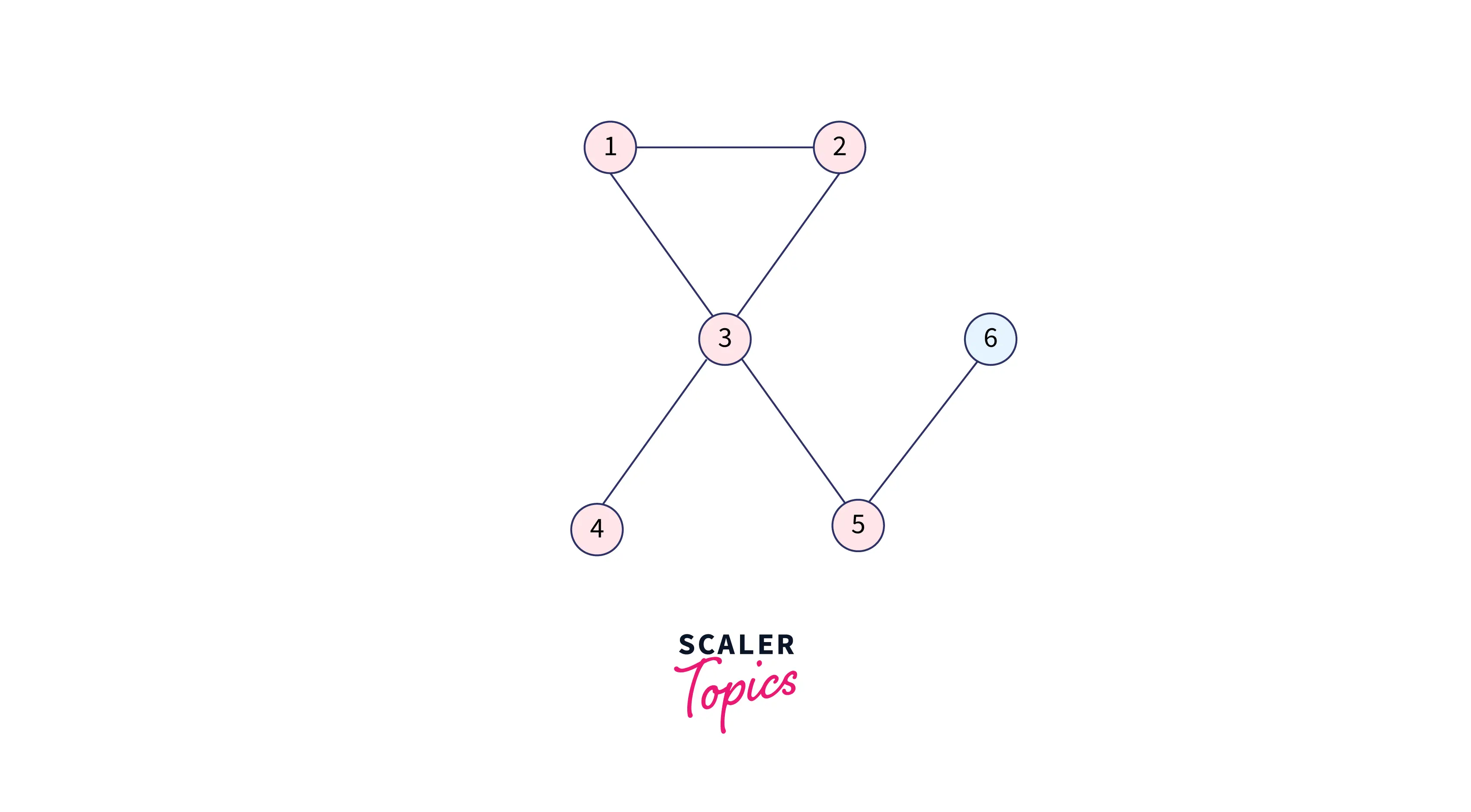
Queue: 4 5
Visited: 1 1 1 1 1 0
Now we will process over Node 4, but its connected nodes 3 is already visited so we will simply pop 4 from the queue and process on 5.
Queue: 5
Visited: 1 1 1 1 1 0
For node 5: Node 3 is already visited so we will add 6 to the queue.
Queue: 6
Visited: 1 1 1 1 1 1
For Node 6 the only connected Node is 5 and as it is already visited we will pop node 6 from the queue and the Algorithm will stop here.
The order of the nodes being added in the queue is: 1 2 3 4 5 6.
Now we are going to implement the above-explained example but, before moving to implement we will discuss queues in C. As we have seen that the queue data structure is used to store the nodes which are visited but not proceeded, we need to implement a queue data structure as there is no inbuilt queue data structure present in the C language.
Let’s see the code implementation of the above example:
Output Output for the above BFS implementation in C is:
As per our BFS program in C, our expected output will simply be the order of the nodes by which they are processed or added to the queue.
Explain the Working of the BFS Implementation in C Program
In the above program, we have implemented the BFS algorithm in C for that: Firstly, we implemented the queue data structure using an array, and defined two integer variables ‘front’ and ‘back’ to indicate the positions in the array named queue. We created two functions push and pop to perform queue operations:
- push: push function takes a single parameter to push at the end of the queue and increments the end variable by 1.
- pop: pop function pops the front element of the queue by incrementing the front variable by 1.
In the main function first, the adjacency matrix is provided which indicates ith and the jth node are connected or not.
Now our main BFS implementation in C starts: Initially, we added the 1st Node in the queue (as we are going to start BFS from here). Then implemented a while loop that will run until the queue is non-empty or the variable ‘front’ is not equal to ‘back’. In the while loop, we will store the front element of the queue in the current variable and pop it from the queue. We will use for loop to find all the connected nodes of the current node which are not been visited yet and add them to the queue by marking them visited. As we are adding nodes only if they are not visited and removing them at each step, we are going to end the loop with an empty queue that indicates no more connected nodes left.
Time and Space Complexity
- If the graph or tree has N nodes, then by using the BFS algorithm we can travel at most N-1 nodes and for each Node, there are N nodes that may or may not be connected to them and we have to look for them that implies time complexity of the BFS algorithm is O(N*N).
- If the graph or tree has N nodes, in the queue we are not storing the repeated/revisited nodes which means only N nodes can be maximum present in the queue. So, the Space complexity of the BFS algorithm in C is O(N).
Conclusion
- BFS algorithm in C, also known as the Breadth-First Search algorithm is commonly used as a search algorithm in graphs, trees, multidimensional arrays, or in general recursion.
- BFS program in C is implemented by using a queue data structure to perform the basic characteristic of the BFS algorithm that is traversing level-wise.
- The queue is a linear data structure that works on the FIFO(First in First out) property.
- The time complexity of the BFS algorithm in C is O(N*N) and the space complexity of BFS implementation in C is O(N), where N is the number of nodes.
- DFS algorithm has a chance to be stuck in infinite search and it may never provide a solution but the BFS algorithm in C always provides the solution.
